AR, VR, MR
Understanding the Difference
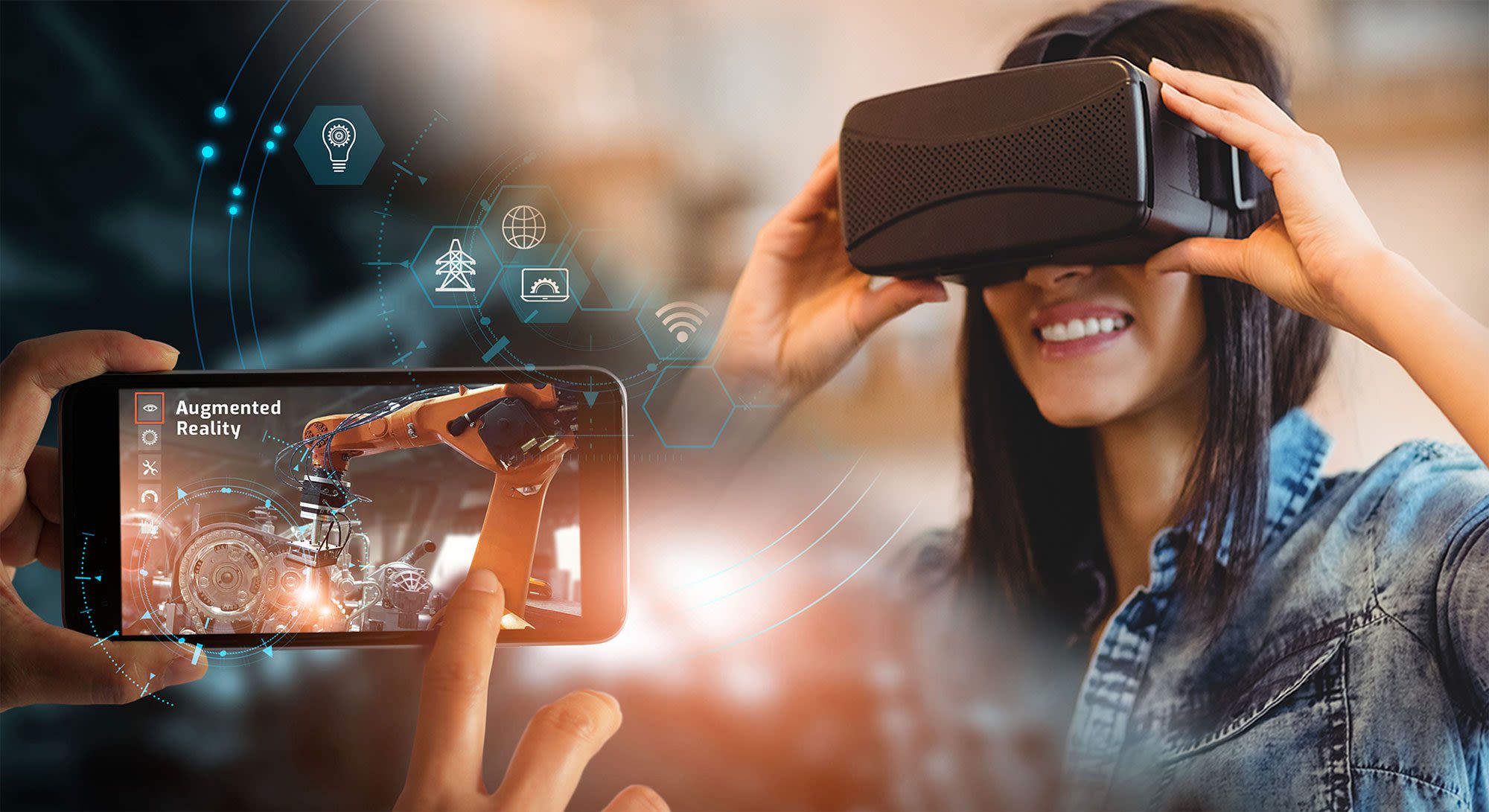
If you’re diving into the world of immersive technology, you’ll often hear about AR, VR and MR. But what do these terms really mean and how do they differ? More importantly, why should you, as a student, care about them?
Here’s a clear breakdown, plus how studying at University Malaysia of Computer Science and Technology (UNIMY) can give you hands-on exposure and real industry relevance.
What Do AR, VR & MR Actually Mean?
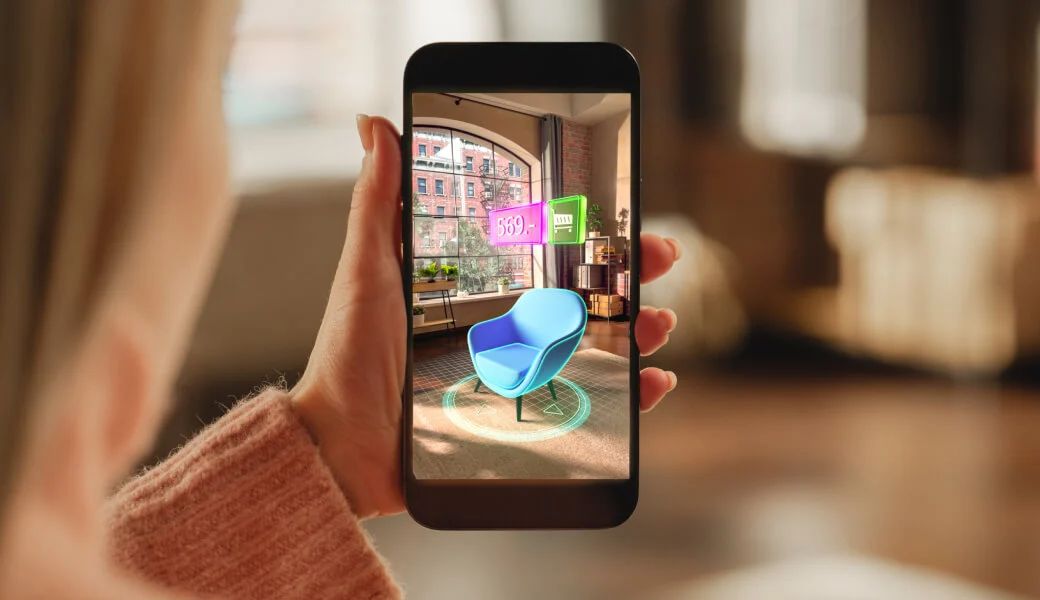
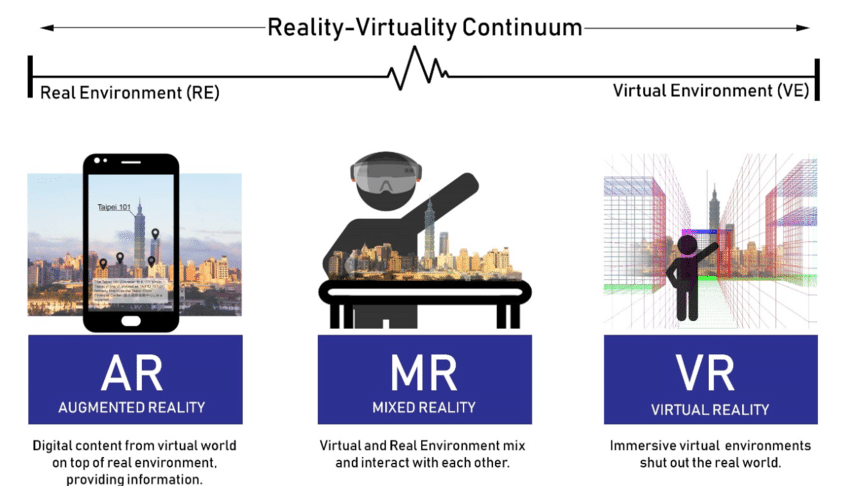
Augmented Reality (AR)
What it is: With AR, virtual objects or information are overlaid onto the real world. Think of digital elements being placed on top of your real surroundings, like navigation arrows appearing on the road through your phone camera or digital characters interacting with your physical space.
Why it's useful: AR enhances your perception of reality, making it a powerful tool for education, retail, maintenance and more. You don’t completely leave your real environment, instead, you enrich it.
Virtual Reality (VR)
What it is: VR creates a fully immersive digital environment that replaces your real-world view. When you strap on a VR headset, you might find yourself in a completely virtual room, a simulated landscape or a fantasy world.
Why it's useful: This level of immersion is invaluable for simulation, training, gaming, design and storytelling. It lets you explore worlds that don’t exist in the physical world.
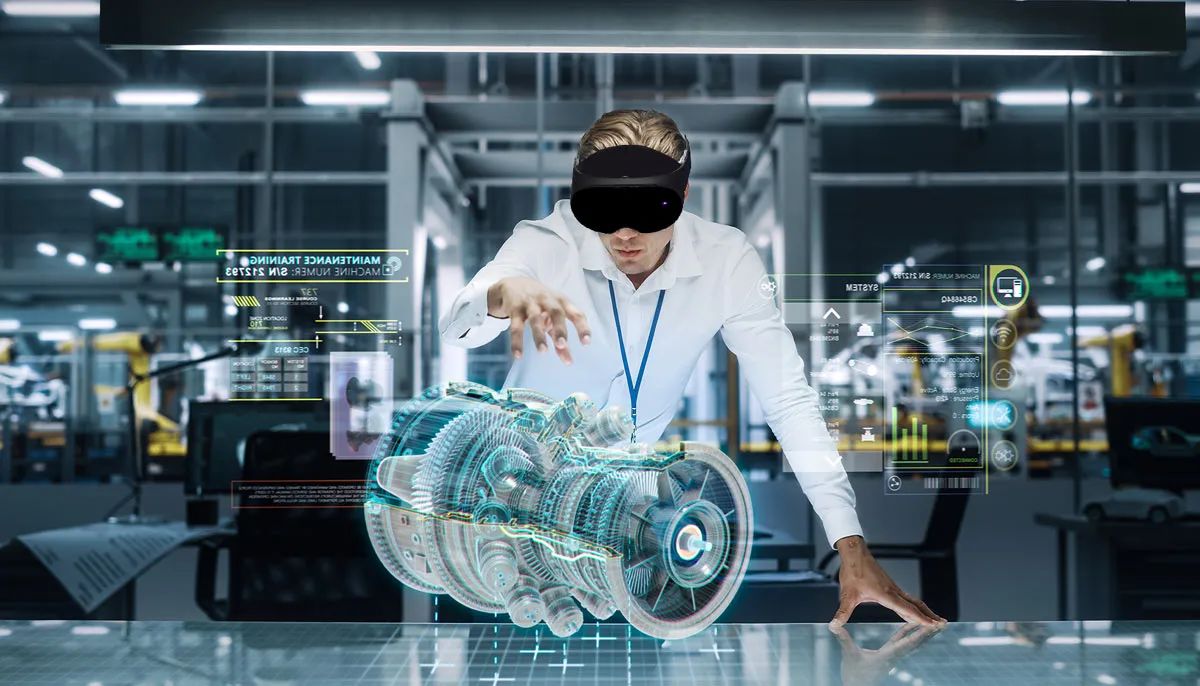
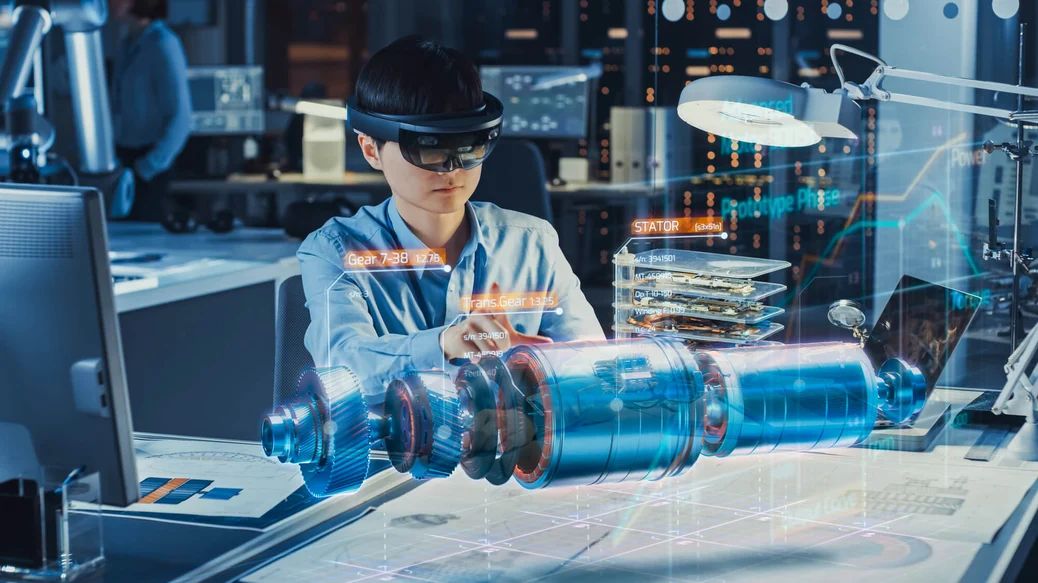
Mixed Reality (MR)
What it is: MR blends the physical and digital worlds in a way that virtual elements interact convincingly with real ones. Unlike AR (which just overlays), MR means digital objects can anchor, respond and behave as though they exist in your real space.
Why it's useful: MR is powerful for collaborative work, design, industrial training and advanced interfaces, because virtual and physical objects coexist and influence each other.
Why These Technologies Matter — Especially in IR 4.0
In today’s era of Industry 4.0, immersive technologies like AR, VR and MR are not just “cool gadgets”, they’re becoming core to innovation:
- Training & Simulation: Companies (from healthcare to aviation) use VR and MR for safe, realistic training without physical risk.
- Design & Prototyping: Product designers and architects use MR to visualise digital prototypes in real space.
- Education & Engagement: AR can make learning far more interactive; for instance, historical sites can be enhanced with digital reconstructions or scientific models can be visualised in 3D.
- Collaboration: Remote teams can meet in virtual or mixed-reality environments, making remote work more immersive.
- Entertainment & Gaming: Immersive media is already reshaping how games, art and storytelling are delivered.
How UNIMY Empowers You to Explore AR, VR & MR
At UNIMY’s School of Computing & Digital Technology, XR (which includes AR, VR and MR) is one of the eight critical digital technology areas that you can specialise in.
Here’s how UNIMY helps you build expertise in these immersive technologies:
If you enroll in the Diploma in Interactive and Digital Media programme, you’ll take modules such as Human-Computer Interaction, 3D Graphics & Animation and Digital Video, which lay the groundwork for XR development.
With the Bachelor of Multimedia (Interactive Media) (Hons), there are dedicated modules like Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality, as well as Responsive Environment Design.
For postgraduate study, the Master in Computing programme includes research areas explicitly tied to AR, VR, UI/UX, game design and interactive applications.
Industry-Relevant Exposure
UNIMY’s School of Computing and Digital Technology works closely with industry partners, including tech giants like Microsoft and AI. These collaborations help you access industry tools, certification opportunities and internship placements where immersive technologies are applied in real business scenarios.
Expert Tech Talks & Workshops
UNIMY regularly invites industry experts and practitioners to give tech talks or lead workshops. These sessions cover the latest XR trends, design principles, hardware and software approaches. Through these events, you learn from professionals working on real-world AR/VR/MR applications — not just theory — and you can ask questions, make connections and get advice relevant to your own projects.
Hands-On Learning
You’ll work in labs and smart classrooms equipped with 3D design tools, motion-capture technology and possibly AR/VR hardware. Through practical coursework and projects, you develop real experience building for immersive platforms. Your assignments might involve designing a virtual environment, creating MR prototypes or implementing interactive AR experiences.
Why You Should Care as a Student
If you specialise in AR, VR or MR:
- Your skills will be in demand: As immersive tech becomes more mainstream, businesses will need developers and designers who understand how to build and deploy XR applications.
- You gain a competitive edge: Being able to create for AR/VR/MR sets you apart from other tech graduates because fewer people have practical experience in immersive development.
- You’re future ready: Whether you go into gaming, simulation, training, architecture or collaborative workspaces, XR opens doors in a variety of industries.
- You can lead innovation: You’ll be among the first to define how humans and digital systems will interact, contributing to future products, services or even new business models.
Understanding the differences between AR, VR and MR is about recognising where technology is headed. These immersive realities are not gimmicks; they’re rapidly becoming central to design, business, education and entertainment.
By studying at UNIMY’s School of Computing & Digital Technology, you position yourself at the forefront of this transformation. With modules tailored to XR, strong industry ties and expert-led learning, you’re not just learning about these technologies, you’re building them.
If you’re ready to shape immersive experiences and step into the future of human-machine interaction, UNIMY has the roadmap. Will you follow it?




